journal-epidemiolInfect-cord
Introduction
This is a Distant Reader "study carrel", a set of structured data intended to help the student, researcher, or scholar use & understand a corpus.
This study carrel was created on 2021-05-30 by Eric Morgan <emorgan@nd.edu>. The carrel was created using the Distant Reader cord process, and the input was the result of a query applied to a local mirror of CORD, a data set of scholarly articles on the topic of COVID-19. The actual query was: facet_journal:"Epidemiol Infect". The results of this query were saved in a cache and transformed into a set of plain text files. All of the analysis -- "reading" -- has been done against these plain text files. For example, a short narrative report has been created. This Web page is a more verbose version of that report.
All study carrels are self-contained -- no Internet connection is necessary to use them. Download this carrel for offline reading. The carrel is made up of many subdirectories and data files. The manifest describes each one in greater detail.
Size
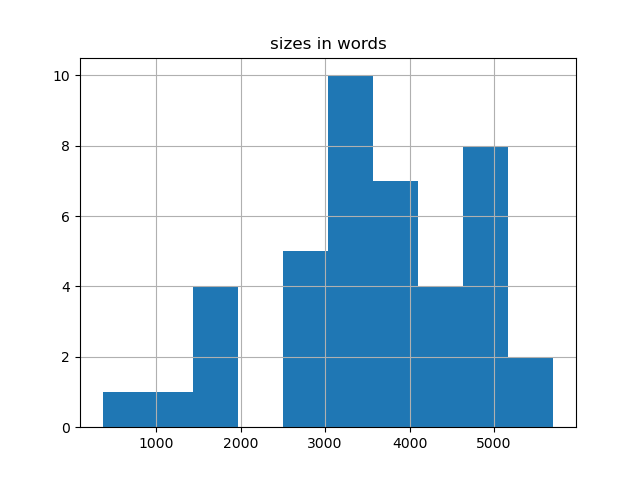
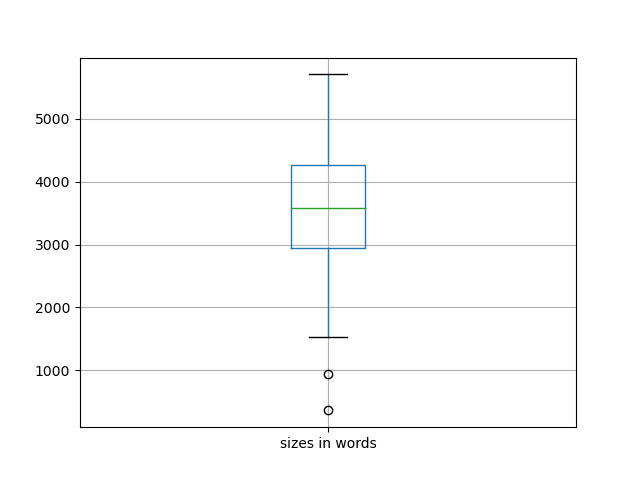
There are 42 item(s) in this carrel, and this carrel is 149,275 words long. Each item in your study carrel is, on average, 3,554 words long. If you dig deeper, then you might want to save yourself some time by reading a shorter item. On the other hand, if your desire is for more detail, then you might consider reading a longer item. The following charts illustrate the overall size of the carrel.
Readability
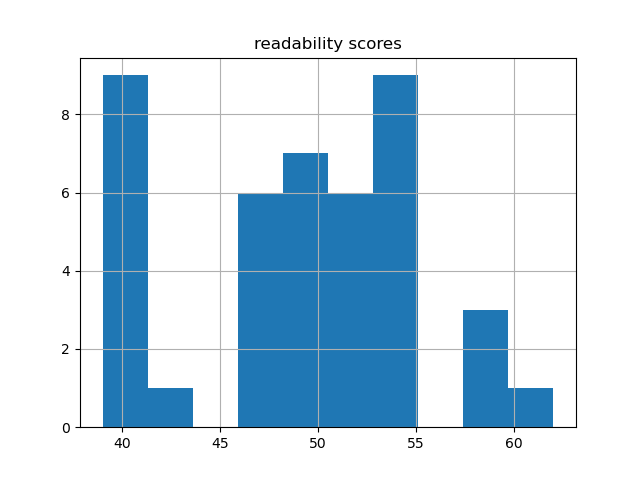
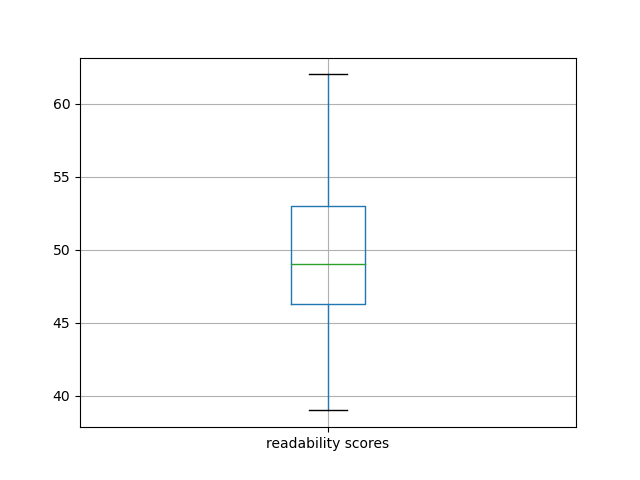
On a scale from 0 to 100, where 0 is very difficult and 100 is very easy, the documents have an average readability score of 49. Consequently, if you want to read something more simplistic, then consider a document with a higher score. If you want something more specialized, then consider something with a lower score. The following charts illustrate the overall readability of the carrel.
Word Frequencies
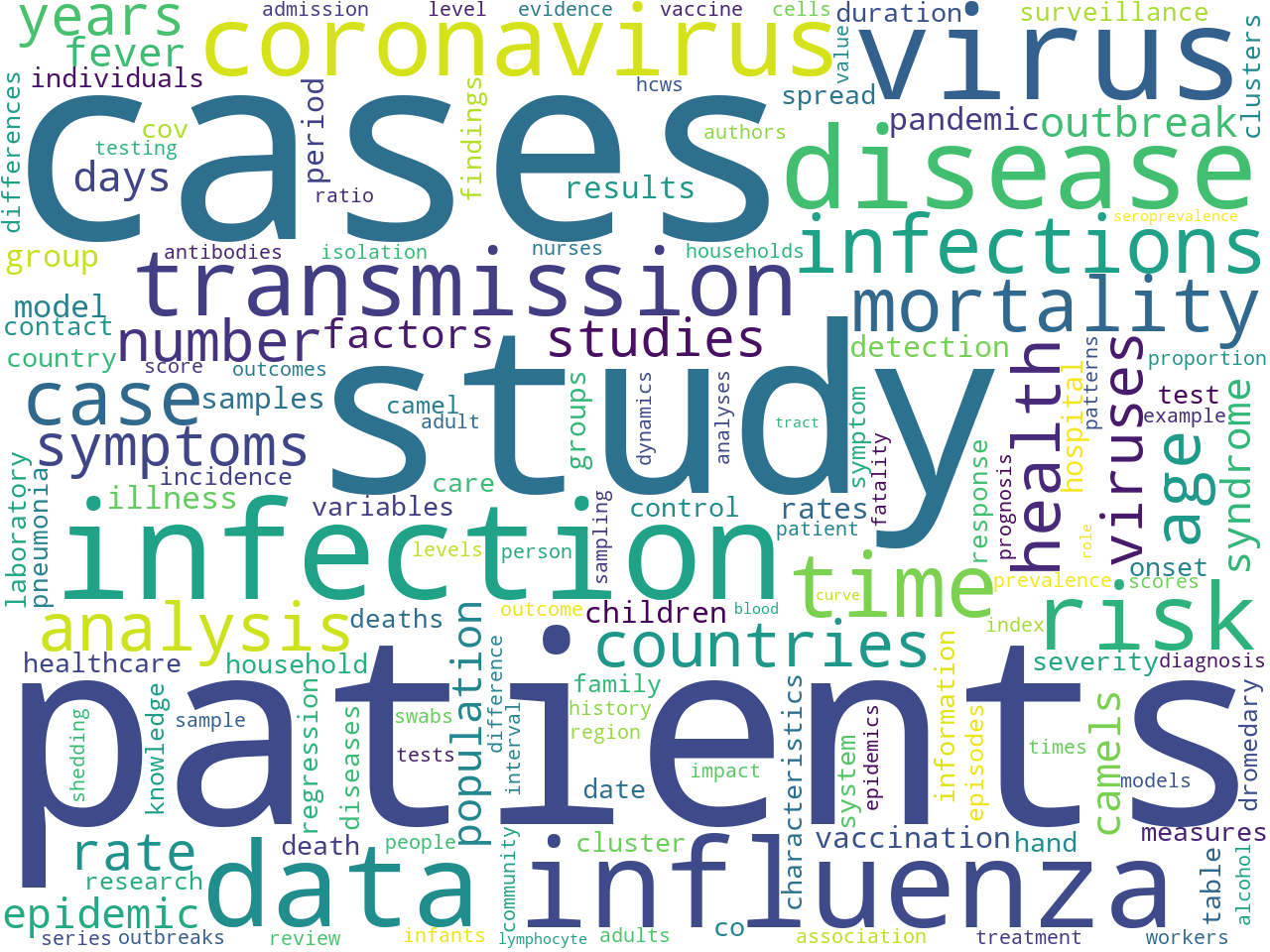
By merely counting & tabulating the frequency of individual words or phrases, you can begin to get an understanding of the carrel's "aboutness". Excluding "stop words", some of the more frequent words include:
covid, cases, patients, respiratory, cov, study, infection, influenza, virus, mers, disease, coronavirus, data, health, risk, transmission, viral, infections, time, sars, case, mortality, analysis, reported, used, age, clinical, viruses, severe, may, symptoms, population, number, also, studies, countries, associated, years, days, one, epidemic, pandemic, two, syndrome, rate, outbreak, camels, fever, illness, rsv
Using the three most frequent words, the three files containing all of those words the most are Ecologic association between influenza and COVID-19 mortality rates in European countries, Descriptive epidemiology of coronavirus disease 2019 in Nigeria, 27 February–6 June 2020, and Knowledge, attitudes and practices of healthcare workers during the early COVID-19 pandemic in a main, academic tertiary care centre in Saudi Arabia.
The most frequent two-word phrases (bigrams) include:
respiratory syndrome, middle east, east respiratory, syndrome coronavirus, public health, respiratory viruses, acute respiratory, coronavirus disease, novel coronavirus, saudi arabia, dromedary camels, risk factors, respiratory syncytial, syncytial virus, severe acute, respiratory virus, mortality rates, respiratory infections, statistically significant, clinical characteristics, influenza vaccination, world health, viral shedding, cov cases, health organization, symptom onset, infect doi, epidemiol infect, cord uid, doc id, viral infection, infectious diseases, respiratory tract, current study, logistic regression, viral infections, study period, healthcare workers, index case, control measures, two groups, mortality rate, virus infection, confirmed cases, hong kong, influenza virus, seasonal influenza, significantly higher, family cluster, respiratory viral
And the three file that use all of the three most frequent phrases are Global status of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in dromedary camels: a systematic review Underlying trend, seasonality, prediction, forecasting and the contribution of risk factors: an analysis of globally reported cases of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus, and New coronavirus outbreak. Lessons learned from the severe acute respiratory syndrome epidemic.
While often deemed superficial or sophomoric, rudimentary frequencies and their associated "word clouds" can be quite insightful:
Keywords
Sets of keywords -- statistically significant words -- can be enumerated by comparing the relative frequency of words with the number of times the words appear in an entire corpus. Some of the most statistically significant keywords in the carrel include:
covid-19, mers, sars, infection, east, virus, rsv, influenza, rna, respiratory, patient, nlr, march, zika, wuhan, vaccination, transmission, tir, symptom, shahroud, risk, pandemic, nigeria, mortality, mobile, middle, kong, jee, isc, illness, ili, hrv, hrp, household, hospital, hong, hev, hedgehog, health, hand, ghsi, fever, family, ericov, ebola, disease, cov, case, canada, bedouin
And now word clouds really begin to shine:
Topic Modeling
Topic modeling is another popular approach to connoting the aboutness of a corpus. If the study carrel could be summed up in a single word, then that word might be covid, and Seasonal influenza vaccination knowledge, risk perception, health beliefs and vaccination behaviours of nurses is most about that word.
If the study carrel could be summed up in three words ("topics") then those words and their significantly associated titles include:
- influenza - Extensive multiplex PCR diagnostics reveal new insights into the epidemiology of viral respiratory infections
- mers - Global status of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in dromedary camels: a systematic review
- patients - Application of ordinal logistic regression analysis to identify the determinants of illness severity of COVID-19 in China
If the study carrel could be summed up in five topics, and each topic were each denoted with three words, then those topics and their most significantly associated files would be:
- influenza, respiratory, virus - Extensive multiplex PCR diagnostics reveal new insights into the epidemiology of viral respiratory infections
- covid, cases, health - The Global Health Security index and Joint External Evaluation score for health preparedness are not correlated with countries'' COVID-19 detection response time and mortality outcome
- patients, covid, severe - Application of ordinal logistic regression analysis to identify the determinants of illness severity of COVID-19 in China
- mers, cov, camels - Global status of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in dromedary camels: a systematic review
- covid, cases, disease - Two complementary model-based methods for calculating the risk of international spreading of a novel virus from the outbreak epicentre. The case of COVID-19
Moreover, the totality of the study carrel's aboutness, can be visualized with the following pie chart:
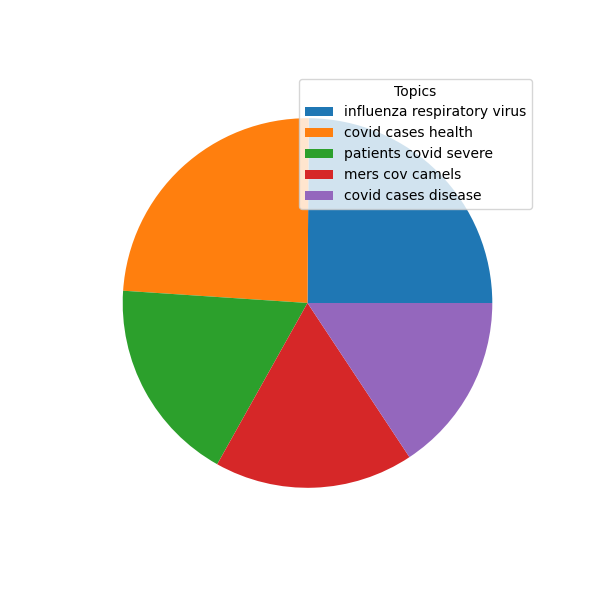
Noun & Verbs
Through an analysis of your study carrel's parts-of-speech, you are able to answer question beyonds aboutness. For example, a list of the most frequent nouns helps you answer what questions; "What is discussed in this collection?":
patients, cases, study, infection, virus, influenza, data, disease, coronavirus, risk, transmission, time, infections, case, mortality, analysis, age, health, countries, symptoms, number, viruses, years, studies, rate, epidemic, population, outbreak, days, camels, syndrome, fever, factors, pandemic, model, illness, group, results, vaccination, rates, detection, samples, children, period, hospital, groups, care, cov, variables, healthcare
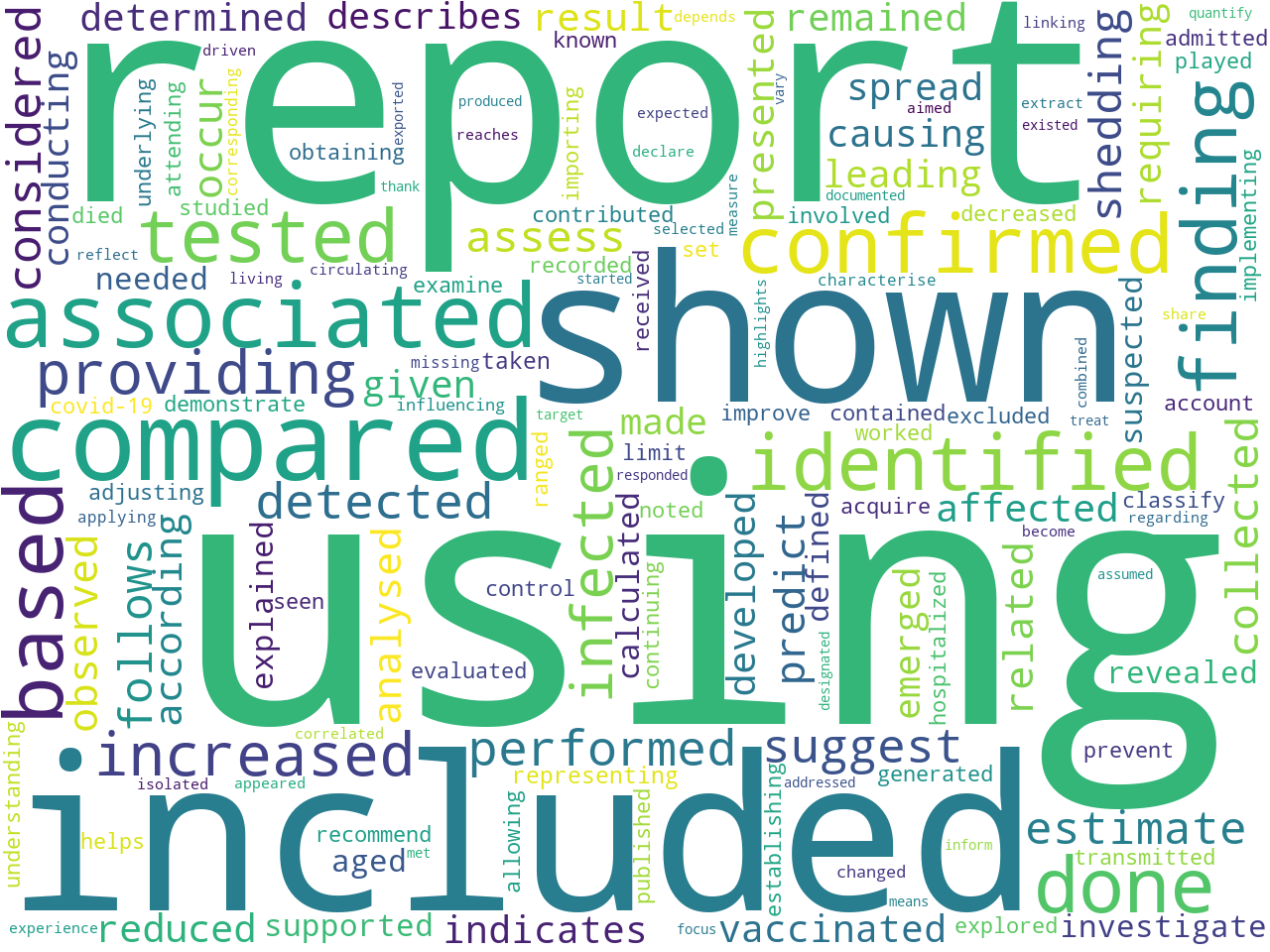
An enumeration of the verbs helps you learn what actions take place in a text or what the things in the text do. Very frequently, the most common lemmatized verbs are "be", "have", and "do"; the more interesting verbs usually occur further down the list of frequencies:
using, report, included, shown, compared, associated, based, confirmed, identified, done, finding, tested, providing, increased, infected, performed, detected, considered, suggest, estimate, follows, collected, assess, shedding, observed, predict, occur, analysed, related, according, result, presented, reduced, developed, affected, vaccinated, requiring, remained, indicates, causing, leading, given, determined, spread, emerged, describes, conducting, made, investigate, supported
Proper Nouns
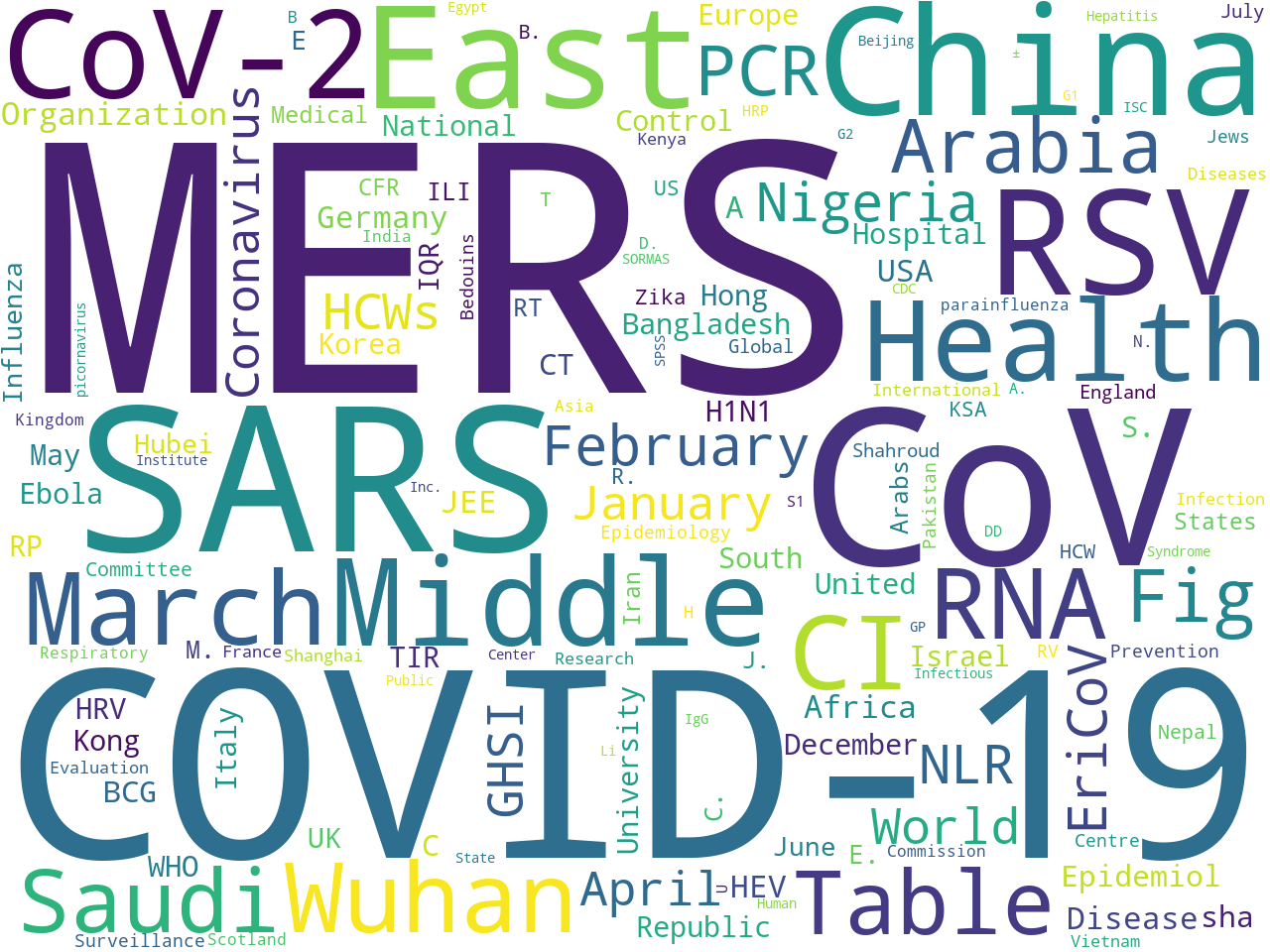
An extraction of proper nouns helps you determine the names of people and places in your study carrel.
MERS, COVID-19, CoV, SARS, China, RSV, East, CoV-2, Middle, Health, CI, March, RNA, Wuhan, Table, Saudi, Arabia, Fig, PCR, February, NLR, EriCoV, Nigeria, World, HCWs, GHSI, January, Coronavirus, April, Organization, Africa, JEE, Germany, Disease, A, USA, HEV, Epidemiol, CT, BCG, sha, Kong, TIR, Hospital, Hong, WHO, H1N1, C, Republic, Europe
An analysis of personal pronouns enables you to answer at least two questions: 1) "What, if any, is the overall gender of my study carrel?", and 2) "To what degree are the texts in my study carrel self-centered versus inclusive?"
we, our, it, their, they, its, them, i, us, his, her, itself, he, she, you, themselves, ourselves, one, him
Below are words cloud of your study carrel's proper & personal pronouns.

Adjectives & Verbs
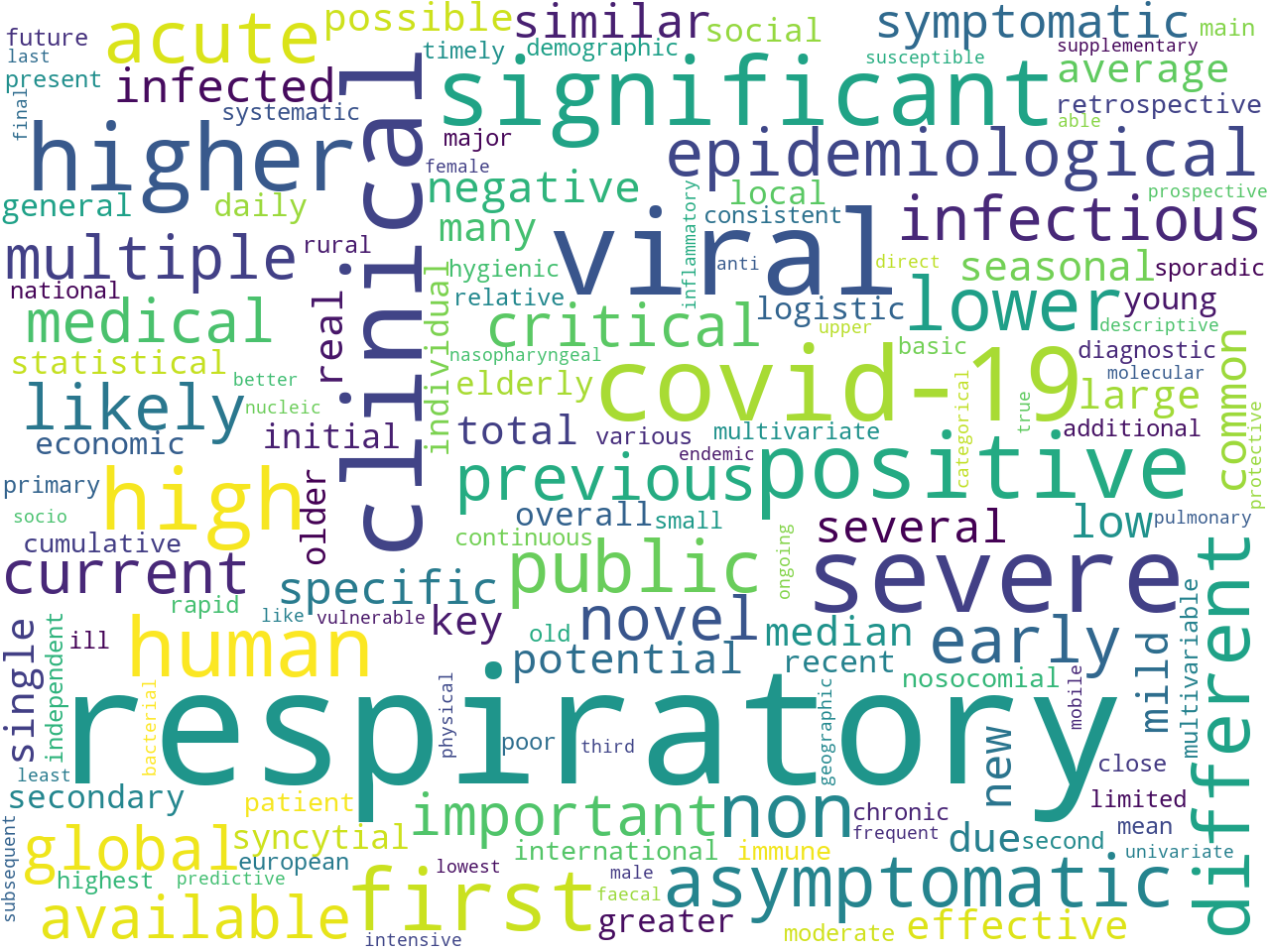
Learning about a corpus's adjectives and adverbs helps you answer how questions: "How are things described and how are things done?" An analysis of adjectives and adverbs also points to a corpus's overall sentiment. "In general, is my study carrel positive or negative?"
respiratory, viral, clinical, severe, covid-19, significant, higher, positive, high, first, human, non, different, lower, acute, public, asymptomatic, epidemiological, early, previous, likely, infectious, novel, global, multiple, medical, current, critical, available, important, symptomatic, similar, specific, infected, common, several, new, low, negative, potential, mild, seasonal, single, average, total, median, large, real, many, key
also, however, significantly, respectively, well, statistically, less, therefore, even, previously, particularly, least, especially, still, worldwide, moreover, often, highly, globally, relatively, prior, first, rapidly, mainly, frequently, critically, commonly, together, similarly, now, never, generally, hence, strongly, potentially, furthermore, overall, likely, additionally, yet, recently, mostly, currently, indeed, specifically, finally, later, probably, fully, effectively
Next steps
There is much more to a study carrel than the things outlined above. Use this page's menubar to navigate and explore in more detail. There you will find additional features & functions including: ngrams, parts-of-speech, grammars, named entities, topic modeling, a simple search interface, etc.
Again, study carrels are self-contained. Download this carrel for offline viewing and use.
Thank you for using the Distant Reader.