Portal:Ancient Rome
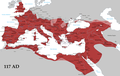
The Ancient Rome portal The Colosseum  A bust of Gaius Julius Caesar In historiography, ancient Rome is Roman civilization from the founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD, encompassing the Roman Kingdom (753 BC–509 BC), Roman Republic (509 BC–27 BC) and Roman Empire (27 BC–476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. The civilisation began as an Italic settlement in the Italian Peninsula, traditionally dated to 753 BC, that grew into the city of Rome and which subsequently gave its name to the empire over which it ruled and to the widespread civilisation the empire developed. The civilization was led and ruled by the Romans, alternately considered an ethnic group or a nationality. The Roman Empire expanded to become one of the largest empires in the ancient world, still ruled from the city, with an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants (roughly 20% of the world's population at the time) and covering 5 million square kilometres (1.9 million square miles) at its height in AD 117. In its many centuries of existence, the Roman state evolved from an elective monarchy to a democratic classical republic and then to an increasingly autocratic semi-elective military dictatorship during the Empire. Through conquest, cultural, and linguistic assimilation, at its height it controlled the North African coast, Egypt, Southern Europe, and most of Western Europe, the Balkans, Crimea and much of the Middle East, including Anatolia, Levant and parts of Mesopotamia and Arabia. It is often grouped into classical antiquity together with ancient Greece, and their similar cultures and societies are known as the Greco-Roman world. Ancient Roman civilisation has contributed to modern language, religion, society, technology, law, politics, government, warfare, art, literature, architecture and engineering. Rome professionalised and expanded its military and created a system of government called res publica, the inspiration for modern republics such as the United States and France. It achieved impressive technological and architectural feats, such as the construction of an extensive system of aqueducts and roads, as well as the construction of large monuments, palaces, and public facilities. The Punic Wars with Carthage were decisive in establishing Rome as a world power. In this series of wars, Rome gained control of the strategic islands of Corsica, Sardinia, and Sicily; took Hispania (modern Spain and Portugal); and destroyed the city of Carthage in 146 BC, giving Rome supremacy in the Mediterranean. By the end of the Republic (27 BC), Rome had conquered the lands around the Mediterranean and beyond: its domain extended from the Atlantic to Arabia and from the mouth of the Rhine to North Africa. The Roman Empire emerged with the end of the Republic and the dictatorship of Augustus. Seven-hundred and twenty-one years of Roman–Persian Wars started in 92 BC with the first struggle against Parthia. It would become the longest conflict in human history, and have major lasting effects and consequences for both empires. Under Trajan, the Empire reached its territorial peak. It stretched from the entire Mediterranean Basin to the beaches of the North Sea in the north, to the shores of the Red and Caspian Seas in the East. Republican mores and traditions started to decline during the imperial period, with civil wars becoming a prelude common to the rise of a new emperor. Splinter states, such as the Palmyrene Empire, would temporarily divide the Empire during the crisis of the 3rd century before some stability was restored in the Tetrarchy phase of imperial rule. Plagued by internal instability and attacked by various migrating peoples, the western part of the empire broke up into independent barbarian kingdoms in the 5th century. The eastern part of the empire remained a power through the Middle Ages until its fall in 1453 AD. (Full article...) Selected article -The Roman Empire (Latin: Imperium Romanum [ɪmˈpɛri.ũː roːˈmaːnũː]; Koinē Greek: Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, romanized: Basileía tōn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, Northern Africa, and Western Asia ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a principate with Italy as metropole of the provinces and the city of Rome as sole capital (27 BC – 286 AD). After the military crisis, the empire was ruled by multiple emperors who shared rule over the Western Roman Empire and over the Eastern Roman Empire (also known as the Byzantine Empire). Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until 476 AD, when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople, following the capture of Ravenna by the barbarians of Odoacer and the subsequent deposition of Romulus Augustulus. The fall of the Western Roman Empire to Germanic kings, along with the hellenization of the Eastern Roman Empire into the Byzantine Empire, conventionally marks the end of Ancient Rome and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The predecessor state of the Roman Empire, the Roman Republic (which had replaced Rome's monarchy in the 6th century BC) became severely destabilized in a series of civil wars and political conflicts. In the mid-1st century BC, Julius Caesar was appointed as perpetual dictator and then assassinated in 44 BC. Civil wars and proscriptions continued, culminating in the victory of Octavian, Caesar's adopted son, over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC. The following year Octavian conquered Ptolemaic Egypt, ending the Hellenistic period that had begun with the conquests of Alexander the Great of Macedon in the 4th century BC. Octavian's power then became unassailable, and in 27 BC the Roman Senate formally granted him overarching power and the new title Augustus, effectively making him the first Roman emperor. (Full article...)General imagesThe following are images from various ancient Rome-related articles on Wikipedia.
Selected biography - Modern statue representing Tacitus outside the Austrian Parliament Building Publius (or Gaius) Cornelius Tacitus (/ˈtæsɪtəs/ TASS-it-əs, Latin: [ˈtakɪtʊs]; c. AD 56 – c. 120) was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is considered by modern scholars to be one of the greatest Roman historians. He lived in what has been called the Silver Age of Latin literature, and has a reputation for the brevity and compactness of his Latin prose, as well as for his penetrating insights into the psychology of power politics. The surviving portions of his two major works—the Annals and the Histories—examine the reigns of the emperors Tiberius, Claudius, Nero, and those who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors (69 AD). These two works span the history of the Roman Empire from the death of Augustus, in 14 AD, to 70 AD in the First Jewish–Roman War of 66–73. There are substantial lacunae in the surviving texts, including a gap in the Annals that is four books long. (Full article...)Did you know?
Related portalsTopicsCategoriesSelect [►] to view subcategories
List articlesSelected picture
WikiProjectsThe following WikiProjects are related to Ancient Rome:
Things you can do
Quotes
Associated WikimediaWeb resources
| ||||||